Learn to Read Your French Payslip
What is a Payslip?
In France, a pay slip is a document provided by the employer proving the salary paid to the employee, it details the net salary paid and the social part of the salary via various contributions (retirement, sickness, provident, unemployment, training, CSG, etc.).
When is the Payslip due?
The payslip must be given to the employee at the time of payment of the remuneration, which must take place at least once a month. The employee must keep their payslip order to exercise pension rights.
Is there a unique Payslip model?
There is no official salary slip template. The forms therefore vary according to the companies.
While already existing payslip models are widely used in practice, the law does not impose a standard model. On the other hand, it does impose mandatory statements that must in all cases be mentioned on the document given to the employee.
How is the Payslip delivered?
The payslip is usually sent to the employee by post or delivered directly by hand against a receipt. It can also be sent in the form of an electronic pay slip, the employee nevertheless retaining the right to refuse this dematerialization.
Why is the taxable net more important than the net payable?
The net salary to be paid is the amount the employee receives after deducting all social security contributions….. The net taxable salary differs from the net salary to be paid because all social contributions, which are payable by the employee, are not deductible for the calculation of income tax.
New: Withholding tax at source : Prélèvement à la source PAS
What is the withholding tax « Prèlèvement à la source » PAS
The withholding tax came into effect on 1 January 2019. Income tax is now deducted directly from the payroll of employee taxpayers.
The employees’ pay slip indicates the basis and rate of the withholding tax, the amount paid as well as the amount of the salary that would have been paid before the withholding tax. This net salary before tax is indicated in large print on the pay slip (1.5 times larger than for the other lines).
How can I change the PAS rate on my Payslip?
If the employee wants to change his withholding tax rate, he should not contact his employer, but the tax authorities. The steps are accomplished by accessing his space on the tax site.
I have never worked and it’s my first Payslip, what is the applicable PAS rate?
An employee who starts work and has never filed an income tax return is automatically charged the neutral withholding tax rate, which corresponds to the rate normally applicable to a single person and is calculated only on the basis of the salary alone.
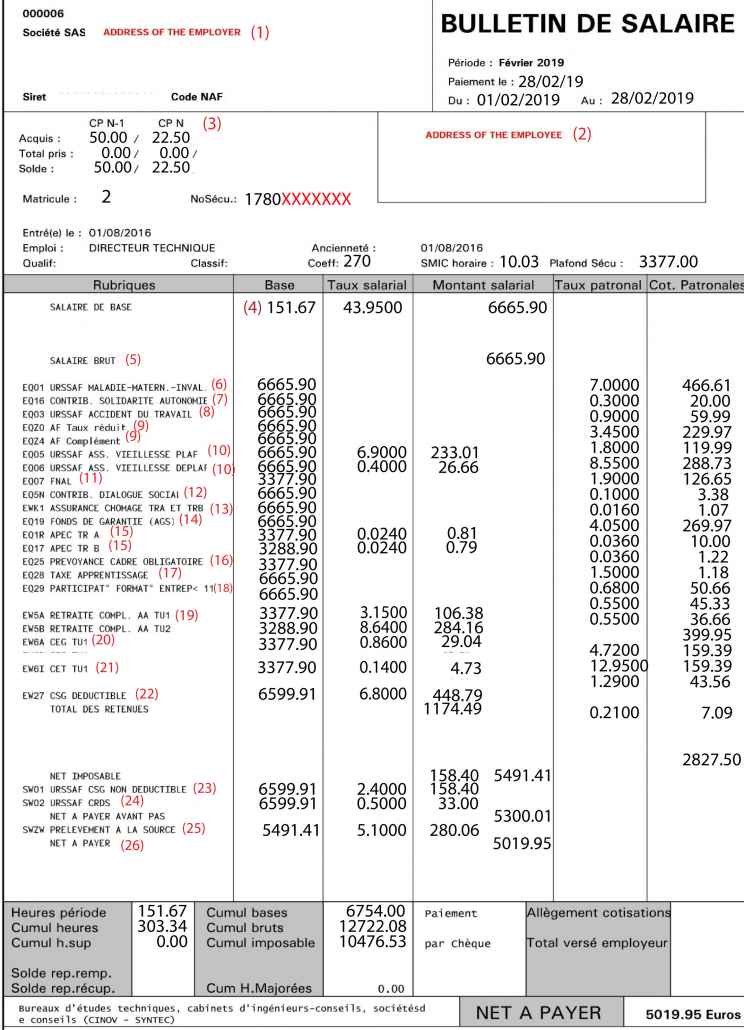
(1) EMPLOYER/ COMPANY
This section contains all the information that the employer must mention, such as the address and name of
the company, etc.
(2) EMPLOYEE
It is mandatory to indicate the employee’s surname, first name, type of job held and the collective
agreement of the branch to which the employer belongs.
(3) PAID LEAVE « Congés payés »
Compulsory counting of earned and available leave days
(4) WORKING HOURS
The first figure corresponds to the number of hours worked in the month and the second to the gross
remuneration corresponding to one hour of work.
(5) GROSS SALARY « Salaire brut »
This is the salary on which contributions or payments to various organizations (social security, pension
funds, etc.) are calculated.
(6) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – HEALTH « Cotisation sociale – Maladie »
The health contribution (maternity, widowhood, invalidity, death) finances the benefits paid in the
event of incapacity for work (daily allowances, reimbursement of care, etc.).
(7) CONTRIBUTION – SOLIDARITY « Contribution – Solidarité »
This contribution is used to finance the autonomy of seniors and people with disabilities.
(This is the famous employer counterpart of Pentecost Monday : Lundi de Pentecôte)
(8) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – WORK-RELATED ACCIDENTS « Cotisation sociale – Accident du travail »
Accident at work: The rate is set for each company according to various criteria (number of employees,
risks specific to the establishment). This contribution covers risks: accidents at work, commuting accidents,
occupational diseases. It is the employer’s expense.
(9) Allocation familiale taux réduit et complémentaire
This contribution is intended to finance the benefits paid by the family allowance funds (CAF).
It is exclusively at the expense of the employer.The contribution for family allowances is calculated on the total remuneration.
(10) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – RETIREMENT PENSION « Cotisation sociale – Vieillesse »
The contribution opens up pension insurance rights. Contribution for your retirement. A part of the
contribution is paid by the employers. The other is at the expense of the employees.
The quarters are determined by taking into account the contributions paid on behalf of the insured.
(11) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – FNAL « Cotisation sociale – FNAL »
It is an employer’s contribution to financing housing assistance for employees.
(12) Contribution dialogue social
This contribution is intended to supplement a joint fund dedicated to the financing of trade union
organisations and professional employer’s organisations.
(13) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – UNEMPLOYMENT INSURANCE « Cotisation sociale – Assurance
chômage »
These are the unemployment insurance contributions. It is used to finance unemployment benefits
(14) Fond de garantie AGS
The AGS contribution, which is only paid by the employer, finances the wage guarantee scheme,
which allows, in the event of the company’s bankruptcy, to guarantee the payment of employees;
remuneration, notice and compensation.
(15) APEC
Employee and employer contribution to APEC (Association for the Employment of Executives), for
executives only.
(16) Prévoyance cadre obligatoire
Employers are required to take out a pension plan for executives and similar executives. This
obligation concerns the life-insurance guarantee, with a contribution to be paid by the employer.
(17) Taxe d’apprentissage
It is used to finance the expenses of apprenticeships and technological and vocational training by
companies.
(18) Participation formation entreprise inf 11
Any company employing employees is covered by participation in professional training, the amount
of which depends on the number of employees in the company and the total wage bill.
Companies with less than 11 employees: 0.55% of the total payroll;
(19) SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION – AGFF RETIREMENT PENSION « Cotisation sociale – Retraite Agff »
These contributions ensure the financing of the supplementary pension
These contributions are paid to the Association pour la gestion de fonds de financement (AGFF), which
finances the supplementary pension.
(20) CEG
It is a new contributions for supplementary pension implemented as from 01/01/2019 the general
equilibrium contribution (gec) is shared 60% by the employer and 40% by the employee.
(21) CET
(Exceptional Temporary Contribution): employee and employer contribution created in 1997 to supplement
the financing of supplementary pensions for executives (Agirc fund).
(22-23) CSG (Contribution Sociale Généralisée) »
It is a tax that pays part of the social security expenses. Its purpose is to reduce the debt of the Social
Security system.
Part of the CSG is deductible from the income tax paid by the taxpayer, the other part is a non-deductible
CSG.
(24) CRDS
The contribution to the reduction of social debt (CRDS) is a tax created in 1996 to reduce social
security debt.
It is exclusively allocated to the Caisse d’amortissement de la dette sociale (CADES), which aims to
eliminate the debt of social security institutions in 2025.
(25) Prélèvement à la source
Withholding tax is a method of tax collection consisting in having the amount of tax deducted by a
third party payer, usually the employer at the time of payment to the taxpayer of the income to
which the tax relates
(26) NET SALARY « Salaire net »
This is the money that the employee actually receives in his bank account